您现在的位置是: 首页 > 车型推荐 车型推荐
汽车制动的理解,汽车制动原理翻译成英文怎么说
tamoadmin 2024-05-30 人已围观
简介1.车辆电子制动力缩写英文2.请帮忙将几个专业课程名称翻译成英文,谢谢3.刹车 ebs 是什么4.求制动系统的英文翻译5.汽车英语缩写大全ABS目录ABS 防抱死制动系统ABS的应用ABS的功用走出ABS误区ABS使用常识ABS函数ABS塑料资产支持证券[编辑本段]ABS 防抱死制动系统“ABS”中文译为“防锁死刹车系统”.它是一种具有防滑、防锁死等优点的汽车安全控制系统。ABS是常规刹车装置基础
1.车辆电子制动力缩写英文
2.请帮忙将几个专业课程名称翻译成英文,谢谢
3.刹车 ebs 是什么
4.求制动系统的英文翻译
5.汽车英语缩写大全
ABS目录
ABS 防抱死制动系统
ABS的应用
ABS的功用
走出ABS误区
ABS使用常识
ABS函数
ABS塑料
资产支持证券
[编辑本段]ABS 防抱死制动系统
“ABS”中文译为“防锁死刹车系统”.它是一种具有防滑、防锁死等优点的汽车安全控制系统。ABS是常规刹车装置基础上的改进型技术,可分机械式和电子式两种。现代汽车上大量安装防抱死制动系统,ABS既有普通制动系统的制动功能,又能防止车轮锁死,使汽车在制动状态下仍能转向,保证汽车的制动方向稳定性,防止产生侧滑和跑偏,是目前汽车上最先进、制动效果最佳的制动装置。
以前消费者买车,都把有没有ABS作为一个重要指标。随着技术的发展,目前,我国绝大部分轿车已经将ABS作为标准配置。但对于ABS的认识以及如何正确使用,很多驾驶员还不是很清楚,甚至还出现了一些对ABS的误解。一些驾驶员认为ABS就是缩短制动距离的装置,装备ABS的车辆在任何路面的制动距离肯定比未装备ABS的制动距离要短,甚至有人错误地认为在冰雪路面上的制动距离能与在沥青路面上的制动距离相当;还有一些驾驶员认为只要配备了ABS,即使在雨天或冰雪路面上高速行驶,也不会出现车辆失控现象。 ABS并不是如有些人所想的那样,大大提高汽车物理性能的极限。严格来说,ABS的功能主要在物理极限的性能内,保证制动时车辆本身的操纵性及稳定性。同时,在加速的时候,也能防止轮胎的纯滑移,提高了加速性能和操作稳定性。
[编辑本段]ABS的应用
ABS的全名是Anti-lock Brake System(防锁死制动系统)或Anti-skid Braking System(防滑移制动系统),它能有效控制车轮保持在转动状态,提高制动时汽车的稳定性及较差路面条件下的汽车制动性能。ABS通过安装在各车轮或传动轴上的转速传感器不断检测各车轮的转速,由计算机算出当时的车轮滑移率,并与理想的滑移率相比较,做出增大或减小制动器制动压力的决定,命令执行机构及时调整制动压力,以保持车轮处于理想制动状态。
1906年ABS首次被授予专利,1936年博世注册了一项防止机动车辆车轮抱死的“机械”专利。所有的早期设计都有着同样的问题:因过于复杂而容易导致失败,并且它们运作太慢。1947年世界上第一套ABS系统首次应用于B-47轰炸机上。Teldix公司在1964年开始研究这个项目,其ABS研究很快被博世全部接管。两年内,首批ABS测试车辆已具有缩短制动距离的功能。转弯时车辆转向性和稳定性也被保证,但当时应用的大约1000个模拟部件和安全开关,这意味着被称为ABS 1系统的电子控制单元的可靠性和耐久性还不能够满足大规模生产的要求,需要改进。博世在电子发动机管理的发展过程中获得的技术,数字技术和集成电路(ICs)的到来使电子部件的数量降低到140个。
1968年ABS开始研究应用于汽车上。1975年由于美国联邦机动车安全标准121款的通过,许多重型卡车和公共汽车装备了ABS,但由于制动系统的许多技术问题和卡车行业的反对,在1978年撤消了这一标准。同年博世作为世界上首家推出电子控制功能的ABS系统的公司,将这套ABS 2的系统开始安装作为选配配置,并装配在梅赛德斯-奔驰S级车上,然后很快又配备在了宝马7系列豪华轿车上。在这一时期之后美国对ABS的进一步研究和设计工作减少了,可是欧洲和日本的制造厂家继续精心研制ABS。
进入20世纪80年代以后,由于进口美国的汽车装备有ABS,美国汽车制造厂对美国汽车市场上的ABS显示出新的兴趣。随着微电子技术的飞速发展和人们对汽车行车安全的强烈要求,ABS装置在世界汽车行业进一步得到广泛应用。1987年美国大约3%的汽车装备有非常可靠的ABS。在随后的时间里,研发者集中于简化系统。在1989年,博世的工程师成功地将一个混合的控制单元直接附在了液压模块上。这样他们就无需连接控制单元和液压模块的线束,也无需接插件,所以显著地减轻了ABS 2E的整体重量。
博世的工程师在1993年,使用新的电磁阀创造了ABS 5.0,并且在后来的几年研发了5.3 和5.7 版。新一代的ABS 8的主要特性是再次极大地减轻了重量、减少了体积、增大了内存,同时增加了更多功能,如电子分配制动压力,从而取代了减轻后轴制动压力的机械机构。当年有些汽车工业分析专家预言得到了证实:到20世纪90年代中期以后,世界市场上的大多数汽车和卡车将装备ABS。
[编辑本段]ABS的功用
ABS的主要作用是改善整车的制动性能,提高行车安全性,防止在制动过程中车轮抱死(即停止滚动),从而保证驾驶员在制动时还能控制方向,并防止后轴侧滑。其工作原理为:紧急制动时,依靠装在各车轮上高灵敏度的车轮转速传感器,一旦发现某个车轮抱死,计算机立即控制压力调节器使该轮的制动分泵泄压,使车轮恢复转动,达到防止车轮抱死的目的。ABS的工作过程实际上是“抱死—松开—抱死—松开”的循环工作过程,使车辆始终处于临界抱死的间隙滚动状态,有效克服紧急制动时由车轮抱死产生的车辆跑偏现象,防止车身失控等情况的发生。
ABS的种类可分机械式和电子式两种。机械式ABS结构简单,主要利用其自身内部结构达到简单调节制动力的效果。该装置工作原理简单,没有传感器来反馈路面摩擦力和轮速等信号,完全依靠预先设定的数据来工作,不管是积水路面、结冰路面或是泥泞路面和良好的水泥沥青路面,它的工作方式都是一样的。严格地说,这种ABS只能叫做 “高级制动系统(Advanced Brake System)”。目前,国内只有一些低端的皮卡等车型仍在使用机械式ABS。
机械式ABS只是用部件的物理特性去机械的动作,而电子式ABS是运用电脑对各种数据进行分析运算从而得出结果的。电子式ABS由轮速传感器、线束、电脑、ABS液压泵、指示灯等部件构成。能根据每个车轮的轮速传感器的信号,电脑对每个车轮分别施加不同的制动力,从而达到科学合理分配制动力的效果。
最早的ABS系统为二轮系统。所谓二轮系统就是将ABS装在汽车的两个后轮上。由于两后轮公用一条制动液压管路和一个控制阀,所以又称做“单通道控制系统”。这种系统是根据两个后车轮中附着力较小的车轮状态来选定制动压力,这被称为“低选原则”。也就是说,采用低选原则的ABS车辆的一个后轮有抱死趋势时,系统只能给两个后轮同时泄压。又由于前轮没有防抱死功能,因而,二轮系统难以达到最佳制动效果。
随着相关技术的发展,后来出现了“三通道控制系统”,该系统是在二轮系统基础上,将两前轮由两条单独的管路独立控制。虽然后轮还是采用“低选原则”,但由于实现了紧急制动时的转向功能及防止后轴侧滑的功能,所以这种系统具备了现代ABS的主要特点。至今,市面上还有车辆采用这种三通道控制的ABS系统。
目前,装备在车辆上最常见的是四传感器四通道ABS系统,每个车轮都由独立的液压管路和电磁阀控制,可以对单个车轮实现独立控制。这种结构能实现良好的防抱死功能。
[编辑本段]走出ABS误区
开篇中那些对ABS的误解,需要解释一下。如果汽车车轮在制动时抱死,汽车能得到的侧向附着力是最小的。这时,由于路面附着系数的不平衡、汽车本身制动力的不平衡、悬架的不平衡、汽车轮胎气压、路面弯度、颠簸或坡度等因素都可能会使汽车发生侧滑、甩尾或失控。另外,由于车辆前轮抱死,汽车会失去转向能力。一个性能优良的汽车防抱死制动系统,在制动时能够将汽车车轮的滑移率控制在20%~30%之间,车轮在这种状态下,能兼顾相对最大的纵向制动力和横向抓地力,有效地保证车辆不会发生失控状况。另外,在前轮不抱死的情况下,由于有一定的抓地力,汽车还可以按照驾驶员的意愿进行转向,从而控制车辆。为了将车轮滑移率控制在理想状态下,追求车辆的稳定性,可能会牺牲一些纵向的制动力。所以,ABS起作用时,不是在所有路面上制动距离都会缩短。
在冰雪路面上,由于地面提供的附着力比一般路面要小很多。ABS只能在这种附着力的基础上调节汽车的制动力,不会产生外加的制动因素。所以,在冰雪路面上的制动距离只能说比车轮抱死时短一些,比在一般路面上的制动距离还是长很多。
实际道路其实是很复杂的,诸如:路面附着系数不平衡、道路弯度或路面横向坡度、甚至汽车轮胎气压等汽车自身的原因,有很多因素能使汽车在制动时产生侧滑的运动趋势,这些因素都不是ABS本身能够克服的。所以,如果在冰雪路面上车速过快时紧急制动,遇到上述因素之一,当车辆离心力大于地面能够提供的最大侧向力时,就会使车辆形成失控趋势,这是非常危险的。
总之,任何装备都不是万能的,驾驶员必须通过自己的主观能动性实现安全驾驶。即使是性能优良的ABS在工作状态下稳定车辆的效果也是有限的,尤其是行驶在砂石路或冰雪路面上,更应保持充分的车距,减速慢行,不要完全依赖ABS系统。
[编辑本段]ABS使用常识
现在基本上所有的乘用车都加装了ABS系统,对提升车辆的主动安全性能起到了很大的作用,但若使用不当,效果也会大打折扣。在这里,我们对ABS的使用原则归纳为“四要、七不要”。
四要
1.要始终踩住制动踏板不放松,这样才能保证足够和持续的制动力,使ABS有效地发挥作用。
2.要保持足够的安全车距。一般情况下,最小车距不应低于50m,当车速超过50km/h时,最小车距与车速数值相同,如100km/h时最小车距为100m,120km/h时,最小车距为120m。
3.要事先熟悉ABS,使自己对ABS工作时的制动踏板抖动有准备和适应能力。
4.要事先阅读汽车驾驶员手册,从而进一步地理解安装ABS的汽车生产厂提供的各种操作说明。
七不要
1.不要认为有了ABS就可以随心所欲地驾驶。ABS也不是绝对保险的,在车速过高和转弯过急的情况下,若车辆制动得过急过猛,则汽车仍然会产生侧滑。因此,即使你的汽车装有ABS,你也仍然需要谨慎驾驶。
2.不要采用“点刹”制动。未装有ABS的车辆在湿滑路面及车速较高情况下实施制动时,需要采用“点刹”的办法达到安全制动的目的。而装上ABS后,由于ABS能自动调整制动力,因此在实施紧急制动时,可一脚将踏板踩到底而不松开,不要担心车轮抱死打滑,否则将大大延长制动距离。
3.不要被ABS的抖动吓住。ABS在起作用时,会听到它发出的噪音,该噪音是由液压控制系统中的电磁阀和液压泵工作时产生的,不要以为制动系统出了毛病而惊慌失措,更不可将脚从制动踏板上移开,这时仍然要将制动踏板踩死而不去管它。
4.不可忽视ABS指示灯的检查。正常情况下,按通点火开关后,此灯应亮;大约3秒后自动熄灭。这一过程,实质上是电子控制装置在按自检程序对车轮传感器、液压调节器的控制阀进行通电检查,若此灯一直不亮,说明ABS有故障。
5.ABS指示灯不熄灭时不必恐慌。当行车中ABS出现故障时,防抱死制动系统自动将原制动系统的油路接通,汽车上的原制动系统仍然工作,只是没有了ABS,注意检修就可以了。
6.不可私自拆换ABS的电脑单元。如果电脑发现故障,应更换整个ABS单元。
7.对于装配了ABS,但是希望改装的车辆,请勿拆装制动管路与ABS单元连接的螺母。
ABS又分电子式ABS和机械式ABS
1、电子式ABS是根据不同的车型所设计的,它的安装需要专业的技术力量,如果换装至另一辆车就必须改变它的线路设计和电瓶容量,没有通用性;机械式ABS的通用性强,只要是液压刹车装置的车辆都可使用,可以从一辆车换装到另一辆车上,而且安装只要30分钟。
2、电子式ABS的体积大,而成品车不一定有足够的空间安装电子ABS,相比之下,机械式的ABS的体积较小,占用空间少。
3、电子式ABS是在车轮锁死的刹那开始作用,每秒钟作用6~12次;机械式ABS在踩刹车时就开始工作,根据不同的车速,每秒钟可作用60~120次。
机械式ABS的适用特性需要事先设定,在积水路面、冰雪路面、沙石路面、沥青路面上,轮胎的摩擦系数不同,车速不同,需要的制动力也不相同。没有即时的测量回馈系统,只依靠预先设定的阕值,适用范围较窄,制动效果会有所降低。
在选购机械式ABS防抱死系统时应非常小心。仿造的ABS产品在外观上与真品大同小异,结构也一样,但劣质产品却难以长期承受刹车油的腐蚀与高压,时间一长橡胶还会老化变形,丧失应有的性能。
真品的橡胶阀囊浸泡在刹车油中可承受每平方英寸11000磅的高压且长期不会发生变形。进口机械式ABS的价格在2000元左右,国产的只要200多元。
[编辑本段]ABS函数
C
函数名: abs
功 能: 求整数的绝对值
用 法: int abs(int i);
程序例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
int number = -1234;
printf("number: %d absolute value: %d\n", number, abs(number));
return 0;
}
Pascal
Function Abs( X : Real ) : Longint;
功 能: 求数的绝对值
例:
Begin
{ 语句; { ( X数据类型 ) 输出结果 } }
Writeln( Abs(84.23) ); {(Real) 8.42300000000000E+0001 }
Writeln( Abs(-111222333) ); {(Longint) 111222333 }
Writeln( Abs(-1112223334324445556) ); {(Int64) 1112223334324445556 }
End.
[编辑本段]ABS塑料
ABS塑料
化学名称:丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯共聚物
英文名称:Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene(ABS)
用途:汽车配件(仪表板、工具舱门、车轮盖、反光镜盒等),收音机壳,电话手柄、大强度工具(吸尘器,头发烘干机,搅拌器,割草机等),打字机键盘,娱乐用车辆如高尔夫球手推车以及喷气式雪橇车等
比重:1.05克/立方厘米
燃烧鉴别方法:连续燃烧、蓝底黄火焰、黑烟、浅金盏草味
溶剂实验:环已酮可软化,芳香溶剂无作用
干燥条件:80-90℃ 2小时
成型收缩率:0.4-0.7%
模具温度:25-70℃(模具温度将影响塑件光洁度,温度较低则导致光洁度较低)
融化温度:210-280℃(建议温度:245℃)
成型温度:200-240℃
注射速度:中高速度
注射压力:500-1000bar
特点:
1、综合性能较好,冲击强度较高,化学稳定性,电性能良好.
2、与372有机玻璃的熔接性良好,制成双色塑件,且可表面镀铬,喷漆处理.
3、有高抗冲、高耐热、阻燃、增强、透明等级别。
4、流动性比HIPS差一点,比PMMA、PC等好,柔韧性好。
5、用途:适于制作一般机械零件,减磨耐磨零件,传动零件和电讯零件.
6、同PVC(聚氯乙烯)一样在屈折处会出现白化现象。
成型特性:
1.无定形料,流动性中等,吸湿大,必须充分干燥,表面要求光泽的塑件须长时间预热干燥80-90度,3小时.
2.宜取高料温,高模温,但料温过高易分解(分解温度为>270度).对精度较高的塑件,模温宜取50-60度,对高光泽.耐热塑件,模温宜取60-80度.
3、如需解决夹水纹,需提高材料的流动性,采取高料温、高模温,或者改变入水位等方法。
4、如成形耐热级或阻燃级材料,生产3-7天后模具表面会残存塑料分解物,导致模具表面发亮,需对模具及时进行清理,同时模具表面需增加排气位置。
ABS树脂是目前产量最大,应用最广泛的聚合物,它将PS,SAN,BS的各种性能有机地统一起来,兼具韧,硬,刚相均衡的优良力学性能。ABS是丙烯腈、丁二烯和苯乙烯的三元共聚物,A代表丙烯腈,B代表丁二烯,S代表苯乙烯。
ABS工程塑料一般是不透明的,外观呈浅象牙色、无毒、无味,兼有韧、硬、刚的特性,燃烧缓慢,火焰呈**,有黑烟,燃烧后塑料软化、烧焦,发出特殊的肉桂气味,但无熔融滴落现象。
ABS工程塑料具有优良的综合性能,有极好的冲击强度、尺寸稳定性好、电性能、耐磨性、抗化学药品性、染色性,成型加工和机械加工较好。ABS树脂耐水、无机盐、碱和酸类,不溶于大部分醇类和烃类溶剂,而容易溶于醛、酮、酯和某些氯代烃中。
ABS工程塑料的缺点:热变形温度较低,可燃,耐候性较差。
ABS船级社认证图标
ABS:美国船级社缩写。
[编辑本段]资产支持证券
ABS :资产支持证券(也叫资产担保证券或资产支撑证券,英文:Asset-backed security)由银行、信用卡公司或者其他信用提供者的贷款协议或者应收帐款作为担保基础发行的债券或票据;它与抵押有所不同。
ABS是以非住房抵押贷款资产为支撑的证券化融资方式,它实际上是MBS技术在其他资产上的推广和应运。由于证券化融资的基本条件之一是基础资产能够产生可预期的、稳定的现金流,除了住房抵押贷款外,还有很多资产也具有这种特征,因此它们也可以证券化。随着证券化技术的不断发展和证券化市场的不断扩大,ABS的种类也日趋繁多,具体可以细分为以下品种:(1)汽车消费贷款、学生贷款证券化;(2)商用、农用、医用房产抵押贷款证券化;(3)信用卡应收款证券化;(4)贸易应收款证券化;(4)设备租赁费证券化;(5)基础设施收费证券化;(6)门票收入证券化;(7)俱乐部会费收入证券化;(8)保费收入证券化;(9)中小企业贷款支撑证券化;(10)知识产权证券化等等。而且随着资产证券化技术的不断发展,证券化资产的范围在不断扩展。
车辆电子制动力缩写英文
汽车相关英文
1、 ABS
答:Antilock Braking System 防抱死制动系统
在制动过程中自动控制和调节车轮的制动力大小。防止车轮被抱死,以取得最佳制动效果的装置。
2、ALR
答: Automatic Locking Retractor (safety belt) 自动锁紧(安全带)伸缩器
当安全带受到空发外力时,自动锁紧装置能够自动锁死,确保乘客安全。
3、ASCD
答: Automatic Speed Control Device 车速自动控制装置
能够自动保持一定的车速,减轻驾驶者的操作负担。
4、ASR
答:Automatic Slip Regulation (车轮)防滑控制(调节)
在车辆行驶过程中,保持汽车原有的行驶路线,充分发挥驱动力。防止滑动以获得最佳行驶效果的装置。
5、CAN
答: Controller Area Network 控制器区域网络
将车内控制系统集成控制,减少了车内线束使用,减轻了汽车重量。是现代车上大都采用的系统。
6、CKD
答: Completely Knocked Down 散件进口组装
国内部分品牌车采用的制造方式,将汽车站零部件以散件形式进口。
7、CVT
答: Continuously Variable Transmission 无级变速器
最近开始涌现的一种变速形式,比自动变速更顺畅。
8、DFI
答: Direct Fuel Injectors 直接喷油喷嘴
运用于柴油发动机上。
9、DOHC
答: Double Over Head Camshaft 双凸轮轴
两个顶置凸轮放在汽缸体上。第一个用于带动吸气阀门,第二个用于带动排气阀门。
10、EBD
答: Electronic Break force Distribution 电子制动力分配
根据车辆的重量和路面条件的变化来控制制动过程,自动以前轮为基准去比较后轮轮胎的滑动率,如发觉前后车轮有差异,而且差异程度必须被调整时,它就会调整汽车制动液压系统,使前、后轮的液压接近理想化制动力的分布状况。
11、ECU
答: Engine Control Unit 发动机控制单元
运用微电脑来控制发动机各部分工作配合。
12、ECS
答: Engine Controlling System 发动机控制系统
用电脑控制发动机的各项过程的系统,来把发动机发挥到最好的水平。
13、ECT
答: Electronic Controlled Transmission 电子控制变速器
可以控制车速以及在停车时能按需要锁住变速器。
14、EDC
答: Electronic Diesel Control 柴油机电子控制
类似于发动机控制系统,能够充分发挥柴油机的性能。
15、EFI
答: Electronic Fuel Injection 电子燃油喷射
根据不同的行驶路况和发动机运转负荷来自动调节喷油量的多少。
16、EPS
答: Electrical Power Steering 电动助力转向系统
利用电动机产生的动力协助驾车者进行转向。
17、ESP
答: Electronic Stabilty Program 电控行驶平稳系统
能够探测和分析车况并纠正驾驶的错误,对过度转向或不足转向特别敏感,传感器感觉到滑动就会迅速制动右前轮使其恢复附着力,产生一种相反的转矩而使汽车保持在原来的车道上。
18、FWD
答: Front Wheel Drive 以前轮作为驱动轮形式。
19、GTS
答: Global Telecommunication System 全球无线电通讯系统
无线电通讯系统让驾驶者可以在车上使用车载电话。
20、GPS
答: Global Positioning System 全球定位系统
高级车上辅助驾驶者的导航系统,通过定位卫星来引导驾驶者行车路线,避免拥堵,减少时间。
21、GOA
答: Global Outstanding Assessment 全方位车体吸撞结构
丰田公司开发设计的安全结构,使车体具备最新的正面、侧面防撞性能。
22、HAS
答: Heat Air System 空气加热系统
加热车内空气的系统。
23、i-VTEC
答: Intelligent-variable Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control 可变气门相位及升程系统
针对发动机在不同负荷和转速的需要,通过调节进气门的开启程度及角度,有效地控制进入引擎的汽油及空气比例和分量。
24、ITS
答: Intelligent Transport System 智能交通系统
将先进的信息技术、数据通讯传输技术、电子传感技术、电子控制技术及计算机处理技术等相关技术有效的集成,运用于整个地面交通管理系统,建立一种能在大范围、全方位发挥作用的,实时、准确、高效的综合交通运输管理系统。
25、LCD
答: Liquid Crystal Display 液晶显示
用液晶材料做的显示屏,现被广泛采用,在车上主要是高级影音系统应用。
26、LED
答: Liquid Emitting Diode 发光二极管
越来越多地被运用于汽车上,其体积小、分量轻、坚固,能耗低,寿命长。
27、LNG
答: Liquefied Natural Gas 液化天然气
通过高压将天然气压成液体方便更多储藏,同时便于汽车上携带使用。
28、LPG
答: Liquefied Petroleum Gas 液化石油气
通过高压设备将从石油中提炼的气体压成液体储存,方便携带和使用。
29、MPFI
答: Multi-Point Fuel Injection Module 动力总成控制模块
协调发动机和变速器等动力系统的工作状况,将动力发挥达到最佳工作水平,汽车行驶更加顺畅。
30、PDI
答: Pre-Delivery Inspection 发货(出厂)前检验
每辆车在出厂前都要进行的例行检查,确保质量合格。
31、RWD
答: Rear Wheel Drive 后轮驱动
以后轮作为驱动轮形式,国内目前车辆较少采用。
32、SCS
答: Stop Control System 停车控制系统
一般大型停车场用于科学管理的控制系统。
33、SFI
答: Sequential (port) Fuel Injection 顺序燃油喷射
把燃油按汽缸工作顺序相应喷入进气道,易于控制排放,节省燃油。
34、SKD
答: Semi Knocked Down 零部件进口组装
将整车采用零部件形式进口再进行组装。
35、SOHC
答: Single Over Head Camshaft 单凸轮轴
只有一个顶置凸轮放在汽缸体上,它既带动吸气阀门又带动排气阀门。
36、SRS
答: Supplemental Inflatable Restraint System 安全气囊防护系统
安全气囊防护系统是一个辅助的安全系统,必须配合安全带使用。现在大多是机械触发式设计。
37、TCS
答: Traction Control System 牵引控制系统
通过感应器监测车轮是否滑转。一旦滑转,系统便马上通过调整发动机功率、变速器输出和 ABS制动来改变滑转轮的驱动力,保证在任何情况下都能驾驭自如。
38、VIN
答: Vehicle Identification Number 车辆识别代码
就像人的身份证一样,每一车辆都有独立的一长串数字,其中包含了产地、车型、规格等信息。
39、VTC
答: Variable Timing Control 可变时间控制
控制进所活门的开启和关闭时间,根据发动机的不同负荷,连续调节进气活门的开合角度,令发动机运转顺畅。
也不知道你到底要什么,只好整点跟汽车相关的,对不对你再追问吧
请帮忙将几个专业课程名称翻译成英文,谢谢
车辆电子制动力分配系统缩写为EBD。
英文全称为Electric Brake force Distribution,德文缩写为EBV。所以很多欧洲车用EBV表示,比如奥迪A6、宝来、高尔夫等。
在EBD发明初期,由于其成本高昂,只配备在较高档的汽车中。随着汽车技术的飞速发展,现如今EBD已在绝大部分的乘用车上得到了使用。汽车制动过程中若前轮先抱死滑移,汽车能够维持直线减速停车,处于稳定状态。
EBD电子制动力分配系统实际上是ABS防抱死系统的一个补充功能,在EBD和ABS系统的加持下,车辆急刹车时不仅能获得较短的刹车距离,而且还能避免车身失控。
工作原理
配置了制动力分配(EBD)系统的车辆,在紧急刹车时,车辆四个车轮的刹车卡钳均会动作,以将车辆停下;由于路面状况会有变异,加上减速时车辆重心的转移,四个车轮与地面间的抓地力将有所不同。
制动力分配(EBD)系统的功能就是在汽车制动的瞬间,高速计算出四个轮胎由于附着不同而导致的摩擦力数值,然后调整制动装置,使其按照设定的程序在运动中高速调整,达到制动力与摩擦力(牵引力)的匹配,以保证车辆的平稳和安全。
刹车 ebs 是什么
《汽车构造》Automobile Structure
《汽车设计基础》Basis of Automobile Design
《汽车发动机原理》Principle of Automobile Engine
《汽车运用工程》Automobile Application Engineering
《汽车运行材料》Automobile Operating Material
《车用传感技术》Vehicle Sensing Technology
《汽车贸易》Automobile Trading
《汽车市场营销》Automobile Marketing
《汽车服务企业管理》Management of Auto Service Enterprise
《汽车服务系统规划与企业设计》Auto Service System Planning and Enterprise Design
《汽车保险与理赔》Automobile Insurance and claim
《电子商务概论》Electronic Commerce Conspectus
《机械原理》Mechanical Principle
《制造技术基础》Manufacturing Technology Basis
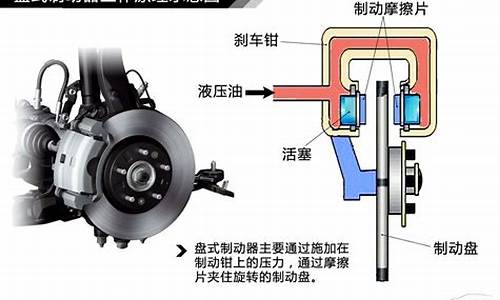
求制动系统的英文翻译
EBS的全称是“Electronic Brake Systems”,顺序翻译就是“电子制动系统”,简称就是EBS。这里需要注意的关键词是“电子”,EBS的关键就是它了,在ABS系统的基础上,EBS增加一套电子控制系统去代替原来的机械系统控制刹车,概括成三个字就是“电控气”。
EBS是基于ABS系统进化而来,也包含了ABS功能,它用电子控制系统取代了原来的纯机械控制,它也可以理解为是电控化的ABS。
EBS不单在性能上得到提升,在功能性上也是全面扩展。所以EBS不只是一个功能单一的系统,它作为工作平台,可以衍生出多种辅助功能,包括车身稳定控制(ESC或ESP)、防侧翻系统(RSC)、驱动防滑(ASR)、坡道辅助(HSA)等等。
扩展资料:
EBS作用:
一、缩短载货汽车的制动反应时间,
载货汽车上通常使用的气压制动系统功能强大,但是对制动板踩下去的反应有一些延迟。而EBS就可以解决这些缺陷,使得重型载货汽车对踩下制动的反应能像轿车一样灵敏。
安装了ABS的气压制动系统可以让时速为96.5km的载货汽车在76.4~85.4m之间完全停住,而安装了EBS制动系统的载货汽车可以将停车距离再缩短15%。
二、增加汽车制动安全性,
汽车制动时,车轮的制动力与地面附着系数有关,当车轮处于半滑动半滚动状态时,地面附着系数可以达到最大,此时的侧向稳定性也较好;当车轮完全抱死无滚动时,地面附着力有所下降,而侧向稳定性为零。极易出现侧滑和甩尾现象,容易造成事故。
汽车电控制动系统EBS是在ABS的基础上,用电子控制取代传统的机械传动来控制制动系统,以达到良好的制动效果,增加汽车制动安全性。
百度百科-EBS
汽车英语缩写大全
制动系统 Braking Systems
由于字数太多所以就不全部粘贴了。
brake is a device for slowing or stopping the motion of a machine or vehicle, or alternatively a device to restrain it from starting to move again. The kinetic energy lost by the moving part is usually translated to heat by friction. Alternatively, in regenerative braking, much of the energy is recovered and stored in a flywheel, capacitor or turned into alternating current by an alternator, then rectified and stored in a battery for later use.
Note that kinetic energy increases with the square of the velocity (E = 1/2·m·v2 relationship). This means that if the speed of a vehicle doubles, it has four times as much energy. The brakes must therefore dissipate four times as much energy to stop it and consequently the braking distance is four times as long.
Brakes of some description are fitted to most wheeled vehicles, including automobiles of all kinds, trucks, trains, motorcycles, and bicycles. Baggage carts and shopping carts may have them for use on a moving ramp.
Some aeroplanes are fitted with wheel brakes on the undercarriage. Some aircraft also feature air brakes designed to slow them down in flight. Notable examples include gliders and some WWII-era fighter aircraft. These allow the aircraft to maintain a safe speed in a steep descent. The Saab B 17 dive bomber used the deployed undercarriage as an air brake.
Deceleration and avoiding acceleration when going downhill can also be achieved by using a low gear; see engine braking.
Friction brakes on cars store the heat in the rotating part (drum brake or disc brake) during the brake application and release it to the air gradually.
Effects on noise pollution
The action of braking for motor vehicles produces recognizable sound level emissions, varying with the specific tire types and with the roadway surface type produces considerable effect upon sound levels or noise pollution emanating from moving vehicles.[1] There is a considerable range in acoustical intensities produced depending upon the specific tire tread design and the rapidity of deceleration required to slow the vehicle.
[edit] See also
Archaic past tense of break (see brake)
Air brake (aircraft)
Air brake (rail)
Air brake (road vehicle)
Bicycle brake systems
Brake-by-wire (or electromechanical braking)
Brake lining
Brake pad
Brake shoe
Bundy tube
Disc brake
Drum brake
Electromagnetic brake
Electronic Parking Brake
Engine braking
Hand brake
Hydraulic brake
Jake brake also known as J braking
Overrun brake
Parking brake
Railway brake
Regenerative braking
Threshold braking
Trail braking
Vehicle brake
---------
How brakes work
Of all the systems that make up your car, the brake system might just be the most important. In the olden days it was also one of the simplest. Over the years as improvements have been made, the system that has evolved isn't so simple anymore... (It's also about a zillion times more reliable and safer.)
Your brakes work as hard or harder than any other part of the car, however much energy it takes to get your car up a hill, it takes at least as much energy to stop it at the bottom. Think about that for a second. Here, I'll say it again, it takes at least as much energy to get your car safely down a hill and stop it at the bottom, as it took to get your car up the hill in the first place. Your brakes do this by converting the kinetic energy to heat energy. All of this heat is generated between the friction surfaces of your brake pads and your rotors. (I am going to disregard the rear brakes for now, since the front brakes do the lion's share of the work.)
Rather than try to give you a step-by-step procedure for repairing your brakes, I'm going to try to show you how to diagnose a few of the many simple brake problems. Unfortunately, before I can do that, I have to talk about how the brake system works. If you already know how it works, then you probably already know what your problem is, but you might find something useful here anyway or at least I hope so.
Brakes operate on a simple hydraulic principle. (See diagram below) If a force is exerted on the piston putting pressure on the fluid confined in the left hand container, the fluid is forced out through the narrow tube at the bottom and into the right hand container, exerting a force on the second piston, forcing it to move upward.
Now this is how the force from your foot gets to the four corners of the car. If we add a lever to magnify the force applied to the first (master) cylinder, and maybe even a power booster unit to increase that force even more, all we have to do next is figure a way to use that force to slow down the wheels. Since the wheels are attached to the car, slowing them down will slow the car.
If we change the shape of the right hand container, (see below) to make something for the piston to push against, we can make it pinch something. Let's bolt a disc(Brake rotor) to the wheel, so that it rotates whenever the wheel does. We'll mount it in such a way that the edge of it is between the caliper piston and the caliper that we have bolted to the axle of the car.so that when the piston moves out, the disc is pinched between it and the other side of the caliper. Actually we're not quite done. As we have the system now, the disc and the caliper would wear out rather quickly (not to mention making horrible grinding/scraping noises). We need to put something between them to protect the surfaces. Let's call this part "Brake Pads" But wait, as we have drawn it, the piston only pushes on one side of the disc. We have to allow the caliper to slide back and forth if we want it to actually pinch the disc efficiently. Let's make an anchor post and allow the caliper to slide along it. Let's make a nice, strong mount to hold the brake pads, and secure it to the axle. Now all we have to do is mount the caliper assembly to some sturdy part of the car and we're in business.
Brake pads have two main parts, the steel backing, and the actual friction material. The backing is only there to support the friction material, which does the actual work of stopping the car. The friction material does it's job by converting the energy of motion to heat energy. This is done by the magic of friction. The friction between the pad and the disc slows down the disc, and creates heat. This heat is transferred to the pad and the disc and then (at some fixed rate) dissipated to the surrounding air. How fast that heat is radiated is determined by a simple formula, depends on mainly two factors, the temperature of the air around the parts, and the flow of air past them. 99% of the time, this cooling is more than enough to keep the brakes cool enough to work just fine.
OK, now we have our simple brake system. Let's see what can go wrong...
Air in the system This is usually caused by air getting into the brake fluid area, usually from the master cylinder. As the brake pads wear, the caliper pistons ride farther out of the caliper, allowing more fluid to remain in the calipers. Over time this can add up to almost as much fluid as there is in the master cylinder reservoir. If neglected, this will allow the master cylinder to pump some air into the brake lines. Air is very compressable, whereas brake fluid is not, as long as there is a solid stream of brake fluid between the master cylinder piston and the caliper piston, the brake pedal will be nice and firm. If there is air in the system, the pedal will feel spongy and will go down almost all the way to the floor, maybe all the way, depending on how much air is in the system. The standard way of dealing with air in the brake system is to perform an operation called "bleeding the brakes".
Hard brake pedal: Can be caused by bad power booster, (or loss of vacuum to the booster) seized caliper pistons, seized caliper slides, pinched brake lines, and (rarely) problems with the pedal linkage under the dash. The probable best fix is rebuilt calipers,and new pads.
Brake fade: I have seen too much of this, having spent 5 years at the bottom of a 13 km hill with 15% grade and continuous switchbacks. Two phenomena contribute to brake fade, one is the fact that the coefficient of friction of most substances gets lower at high temperatures, and that most liquids will boil at some temperature, and that gases compress, while liquids do not. When you use the brakes to decelerate 3,000 or 4,000 or 7-8-15,000 lbs of vehicle, they get hot. Very hot. Under normal circumstances this would be no big deal, the heat that builts up in the pads, rotors, and calipers will slowly radiate back to the air flowing over them as the car continues down the road. But you aren't going down the road, you are back on the brakes, doing more decelerating for the next switchback. Instead of cooling off, your brakes are getting hotter. And hotter, and hotter. . .As the pads and rotors get hotter the friction material of the pads starts to separate. The binding agent starts to boil off from the surface of the pad, plating out on the rotor as a dark, paintlike film...coefficient of friction approaches zero, pedal gets hard, but no braking action. Your pupils dilate to 10 mm and your body goes into fight-or-flight mode, adrenalin courses through your system. But the car just goes faster.... You shift down, now you are standing on the brake pedal with both feet, around this time, the temperature of the brake fluid in the calipers usually reaches it's boiling point and the pedal just sinks to the floor. Your pupils reach 12 mm, your sphyncters contract to pinpoints, somehow you manage to stop the car. There is smoke coming from behind your front wheels, maybe fire. You put out the fire and have lunch. After things cool off you sit in the car and try the brake pedal, it feels almost normal. Congratulations, you've just experienced, (and survived) brake fade. (You've also just flash-fried your front brakes, figure on new everything to fix it properly.)
Brake squeal: This is a high pitched squealing noise, often heard when you are going slow and are not applying the brakes. If it goes away as you apply the brakes, it could be coming from the brake wear sensors. (Also called 'squealers' by mechanics.) They are small bits of spring steel that are attached to the brake pads in such a way that when the pads are about 75% worn out, the sensors start to rub on the rotors, making the noise. GM invented them, and they are one of the best ideas anyone has ever had in the automotive industry. The sound is so scary that you usually go to a mechanic before any major damage is done to your rotors, and before your braking power is compromised, saving you money and maybe your life.
Grinding noise: Although this is one of the nastiest sounds you will ever hear, it often is the easiest to repair. The first thing you must do is learn what is making the noise. Figure out which wheel it is, then, after safely raising and supporting the car, take off the wheel & tire. Hopefully you will see a simple disc brake system, with a rotor, a caliper, and brake pads. Identify the various components. Gently rotate the brake rotor back and forth until you can identify the source of the noise. Sometimes it is just a small stone, trapped between the brake rotor and the air deflector. The faces of the rotor should be smooth and clean. If you see large scaly rusted places on the friction surfaces of the rotor you should replace them. Most of the time new ones cost less than you would guess. If your pads are worn out(less than 3/16 of an inch of friction material left) and you catch it in time, all you have to do is install new brake pads. If the surface of the rotor is damaged, you will have to resurface or replace it.
Brake pedal pulsation: There are a lot of things that can cause this, from out-of-adjustment wheel bearings to rotors that are bent, brake drums that are out-of-round, rusty spots on the rotors that have a different surface smoothness. To determine whether the pulsation is coming from the front or the rear wheels, check to see if you can feel the pulsation in the steering wheel when the pedal is pulsating. If you can, the problem is coming from the front wheels.
Brake pull: Mostly this one comes from either a caliper piston seized or caliper slides seized. This one is dangerous! If your car tries to turn when you apply the brakes you could veer into oncoming traffic. What often happens with this one is this: the caliper piston on one side starts to seize, the other one now applies first, car veers away from bad part. Driver learns to compensate by steering opposite to the pull every time he brakes. A panic situation comes along, driver nails the brakes, steers away from the expected pull, but because the piston was only partially seized, it works just fine when the brakes are applied with vigor. There is no pull this time. It is easy to lose control of your car in situations like this, if your car pulls to one side or the other when you brake, fix it(or get it fixed) before you hurt somebody. Replace calipers and pads and service the caliper slides.
Brake grabbing: When you just barely touch the brake pedal and one or more wheels locks up and skids. This one most commonly comes from contaminated friction material on one or more brakes.
Pedal goes to the floor: Gotta be the scariest of them all. If you're lucky, a quick pump on the pedal will get you some braking action. On most newer cars, there will be some braking just before the pedal reaches the floor. Stop driving and check your fluid level. It might just need to be topped up to temporarily get you some braking action to get you home. Regardless, you must find out what caused it and fix it before you drive any further.
Components
Disc brakes have:
brake calipers
brake pads
rotors
caliper mounting hardware
Drum brakes have:
brake backing plates
brake drums
brake shoe self-adjusters
brake shoes
brake springs
wheel cylinders
Both types use:
Brake fluid
Steel brake lines and reinforced rubber brake hoses
Master cylinder
Power brake booster (usually)
proportioning valve
delay valve
metering valve
brake warning light
park brake cables, levers,
现在很多车辆在购买和维修时会碰到很多的专业英文缩写,很多人碰到这种情况都是一头雾水,所以特地为大家罗列以下汽车上部分常见的元件英文缩写翻译供大家参考(由于个人的水平和时间原因难免会有所差错和遗漏,忘大家加以指正和补充)
Quattro——全时四轮驱动系统
Tiptronic——轻触子-自动变速器
Multitronic——多极子-无级自动变速器
ABC——车身主动控制系统
DSC——车身稳定控制系统
VSC——车身稳定控制系统
TRC——牵引力控制系统
TCS——牵引力控制系统
ABS——防抱死制动系统
ASR——加速防滑系统
BAS——制动辅助系统
DCS——车身动态控制系统
EBA——紧急制动辅助系统
ETS——电子牵引系统
ASR——驱动防滑调整装置
ESP——电子稳定程序
EBD——电子制动力分配系统
EDS——电子差速锁
ESP——电子稳定程序系统
HBA——液压刹车辅助系统
HDC——坡道控制系统
HAC——坡道起车控制系统
DAC——下坡行车辅助控制系统
A-TRC——车身主动循迹控制系统
SRS——双安全气囊
SAHR——主动性头枕
GPS——车载卫星定位导航系统
i-Drive——智能集成化操作系统
Dynamic.Drive——主动式稳定杆
R——直列多缸排列发动机
V——V型汽缸排列发动机
B——水平对置式排列多缸发动机
WA——汪克尔转子发动机
W——W型汽缸排列发动机
Fi——前置发动机(纵向)
Fq——前置发动机(横向)
Mi——中置发动机(纵向)
Mq——中置发动机(横向)
Hi——后置发动机(纵向)
Hq——后置发动机(横向)
OHV——顶置气门,侧置凸轮轴
OHC——顶置气门,上置凸轮轴
DOHC——顶置气门,双上置凸轮轴
CVTC——连续可变气门正时机构
VVT-i——气门正时机构
VVTL-i——气门正时机构
V——化油器
ES——单点喷射汽油发动机
EM——多点喷射汽油发动机
SDi——自然吸气式超柴油发动机
TDi-Turbo——直喷式柴油发动机
ED——缸内直喷式汽油发动机
PD——泵喷嘴
D——柴油发动机(共轨)
DD——缸内直喷式柴油发动机
TA-Turbo——涡轮增压
NOS——氧化氮气增压系统
MA——机械增压
Ap——恒时全轮驱动
Az——接通式全轮驱动
FF——前置引擎前轮驱动
FR——前置引擎后轮驱动
RR——后置引擎后轮驱动
ASM—— 动态稳定系统
AYC——主动偏行系统
ST——无级自动变速器
AS——转向臂
QL——横向摆臂
DQL——双横向摆臂
LL——纵向摆臂
SL——斜置摆臂
ML——多导向轴
SA——整体式车桥
DD——德迪戎式独立悬架后桥
VL——复合稳定杆式悬架后桥
FB——弹性支柱
DB——减震器支柱
BF——钢板弹簧悬挂
SF——螺旋弹簧悬挂
DS——扭力杆
GF——橡胶弹簧悬挂
LF——空气弹簧悬挂
HP——液气悬架阻尼
HF——液压悬架
QS——横向稳定杆
S——盘式制动
Si——内通风盘式制动
T——鼓式制动
SFI——连续多点燃油喷射发动机
FSI——直喷式汽油发动机
PCM ——动力控制模块
EGR——废气循环再利用
BCM ——车身控制模块
ICM——点火控制模块
MAP——空气流量计









